IPV4
X.X.X.X 32 Bits
X=8 Bits
MAC
X.X.X.X.X.X 48 Bits
X=8 Bits
IPV6
X.X.X.X.X.X.X.X 128Bits
X=16 Bits
IP address is an address having information about how to reach a specific host, especially outside the LAN. An IP address is a 32 bit unique address having an address space of 232
Generally, there are two notations in which IP address is written, dotted decimal notation and hexadecimal notation.
Dotted Decimal Notation:
Hexadecimal Notation:
Classful Addressing
The 32 bit IP address is divided into five sub-classes. These are:
Class A
Class B
Class C
Class D
Class E
Each of these classes has a valid range of IP addresses. Classes D and E are reserved for multicast and experimental purposes respectively. The order of bits in the first octet determine the classes of IP address.
IPv4 address is divided into two parts:
Network ID
Host ID
The class of IP address is used to determine the bits used for network ID and host ID and the number of total networks and hosts possible in that particular class. Each ISP (Internet Service Provider) or network administrator assigns IP address to each device that is connected to its network.
Note: IP addresses are globally managed by Internet Assigned Numbers Authority(IANA) and Regional Internet Registries(RIR).
Note: While finding the total number of host IP addresses, 2 IP addresses are not counted and are therefore, decreased from the total count because the first IP address of any network is the network number and whereas the last IP address is reserved for broadcast IP.
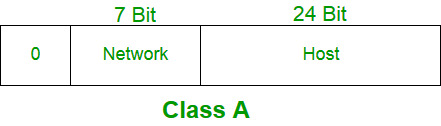
Class A
IP address belonging to class A are assigned to the networks that contain a large number of hosts.
The network ID is 8 bits long.
The host ID is 24 bits long.
The higher order bit of the first octet in class A is always set to 0. The remaining 7 bits in first octet are used to determine network ID. The 24 bits of host ID are used to determine the host in any network. The default subnet mask for class A is 255.x.x.x. Therefore, class A has a total of:
2^7-2= 126 network ID(Here 2 address is subracted because 0.0.0.0 and 127.x.y.z are special address. )
2^24 – 2 = 16,777,214 host ID
IP addresses belonging to class A ranges from 1.x.x.x – 126.x.x.x
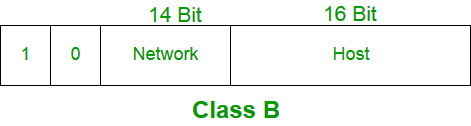
Class B:
IP address belonging to class B are assigned to the networks that ranges from medium-sized to large-sized networks.
The network ID is 16 bits long.
The host ID is 16 bits long.
The higher order bits of the first octet of IP addresses of class B are always set to 10. The remaining 14 bits are used to determine network ID. The 16 bits of host ID is used to determine the host in any network. The default sub-net mask for class B is 255.255.x.x. Class B has a total of:
2^14 = 16384 network address
2^16 – 2 = 65534 host address
IP addresses belonging to class B ranges from 128.0.x.x – 191.255.x.x.
Class C:
IP address belonging to class C are assigned to small-sized networks.
The network ID is 24 bits long.
The host ID is 8 bits long.
The higher order bits of the first octet of IP addresses of class C are always set to 110. The remaining 21 bits are used to determine network ID. The 8 bits of host ID is used to determine the host in any network. The default sub-net mask for class C is 255.255.255.x. Class C has a total of:
2^21 = 2097152 network address
2^8 – 2 = 254 host address
IP addresses belonging to class C ranges from 192.0.0.x – 223.255.255.x.
Class D:
IP address belonging to class D are reserved for multi-casting. The higher order bits of the first octet of IP addresses belonging to class D are always set to 1110. The remaining bits are for the address that interested hosts recognize.
Class D does not posses any sub-net mask. IP addresses belonging to class D ranges from 224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255.
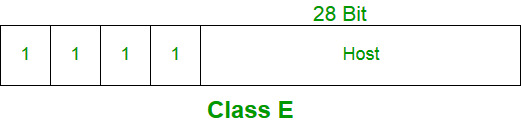
Class E:
IP addresses belonging to class E are reserved for experimental and research purposes. IP addresses of class E ranges from 240.0.0.0 – 255.255.255.254. This class doesn’t have any sub-net mask. The higher order bits of first octet of class E are always set to 1111.
Range of special IP addresses:
169.254.0.0 – 169.254.0.16 : Link local addresses
127.0.0.0 – 127.0.0.8 : Loop-back addresses
0.0.0.0 – 0.0.0.8 : used to communicate within the current network.
Problem :
consider the following subnet mask
255.255.254.0
1)Find the number of hosts per subnet
2)Number of subnet if subnet mask belongs to class A
3)Number of subnet if subnet mask belongs to class B
4)Number of subnet if subnet mask belongs to class C
5)Number of subnet if total 10bits are used for global network ID
















No comments:
Post a Comment